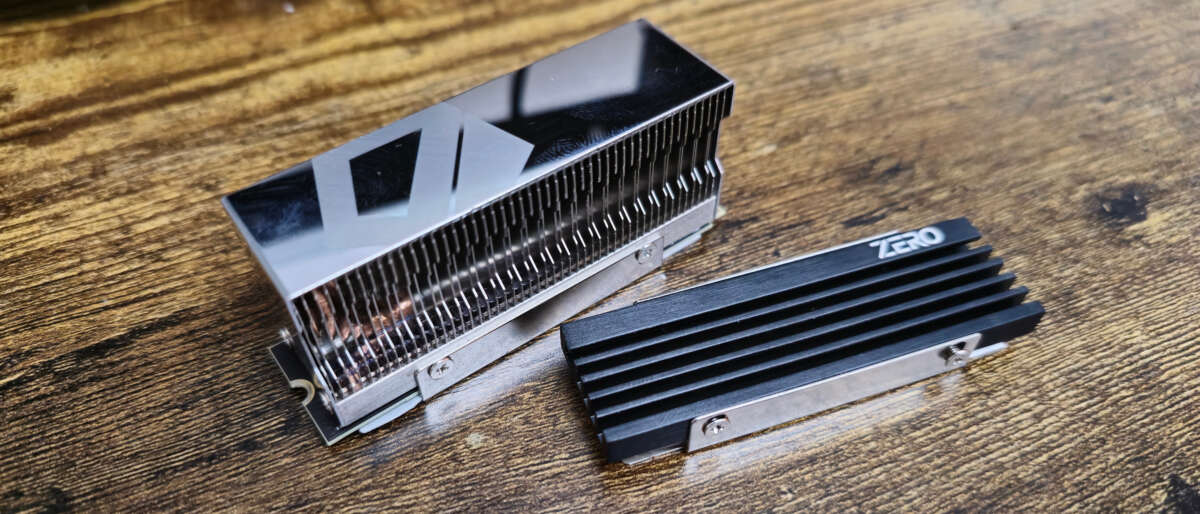
An SSD heatsink is worth it for heavy workloads to prevent performance loss from overheating.
As someone who has built and optimized countless PCs for everything from high-end gaming to professional video editing, I've seen firsthand how a tiny component can become a major performance bottleneck. The question of whether an SSD heatsink is worth it comes up constantly, and the answer isn't always a simple yes or no. It depends entirely on your hardware and how you use it. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, drawing from years of experience and testing, to help you decide if an SSD heatsink is a smart investment for your system.

What is an SSD Heatsink and How Does it Work?
An SSD heatsink is a passive cooling solution designed to draw heat away from the critical components of your solid-state drive. Think of it like a radiator for your car's engine. The engine generates a lot of heat, and the radiator's large surface area helps dissipate that heat into the surrounding air, preventing the engine from overheating. An SSD heatsink works on the same principle.
SSDs, particularly modern NVMe M.2 drives, have two main components that get hot: the controller chip and the NAND flash memory chips. The controller is the "brain" of the drive, managing data flow, and it generates the most heat. A heatsink, typically made of a thermally conductive material like aluminum or copper, makes direct contact with these components via a thermal pad. This allows heat to transfer from the SSD to the heatsink, which then dissipates it into the air moving through your PC case.
By keeping these components cool, a heatsink helps the drive maintain its optimal performance. It is a simple yet effective tool for thermal management. This process is crucial for preventing the drive from reaching temperatures that could negatively impact its speed and potentially its longevity. The effectiveness of a heatsink is a key reason why many people wonder if an SSD heatsink is worth it for their specific setup.

Understanding SSD Temperatures and Thermal Throttling
To truly understand if an SSD heatsink is worth it, you first need to grasp the concept of thermal throttling. Like most high-performance electronics, SSDs have an optimal operating temperature range, typically between 0°C and 70°C (32°F to 158°F). When an SSD is working hard—like during a long gaming session, transferring large files, or rendering a video—its temperature can rise rapidly.
If the temperature exceeds a certain threshold set by the manufacturer, the drive's firmware will automatically reduce its performance to lower heat generation. This safety mechanism is called thermal throttling. It's designed to protect the drive's internal components from damage due to excessive heat. While it’s great for protecting your hardware, it’s not so great for your user experience.
Imagine you're in the middle of a crucial file transfer, and suddenly your transfer speed plummets. Or you're playing a game, and you experience stuttering as the game tries to load new assets from the drive. This is often the result of thermal throttling. An SSD heatsink directly combats this by keeping temperatures in a safe range, allowing the drive to sustain its peak performance for much longer periods.

When is an SSD Heatsink Absolutely Necessary?
Based on my experience building and testing systems, there are several scenarios where I would say an SSD heatsink isn't just a nice-to-have, but a necessity. If you fall into any of these categories, you will see a tangible benefit and find that an SSD heatsink is worth it.
- High-Performance NVMe Drives: Newer PCIe Gen4 and especially Gen5 NVMe SSDs are incredibly fast, but that speed comes at the cost of higher heat output. For these drives, a heatsink is almost always recommended to maintain those advertised speeds.
- Intense Gaming: Modern games with vast open worlds continuously stream assets from your SSD. During long gaming sessions, this sustained workload can cause significant heat buildup, leading to potential performance drops.
- Content Creation: If you are a video editor, 3D artist, or photographer working with large files, your SSD is constantly under heavy load. A heatsink ensures your drive doesn't slow down during critical rendering or file-saving processes.
- Poor Airflow Cases: Compact, Small Form Factor (SFF) PC cases or systems with suboptimal airflow can trap heat. In these environments, an SSD has nowhere to dissipate its heat, making a heatsink essential for reliable operation.
- Large, Sustained File Transfers: Anyone who regularly moves gigabytes of data—whether for backups, project files, or media libraries—will push their SSD to its thermal limits. A heatsink prevents throttling during these long transfers.
I remember testing a new Gen4 drive for a video editing build. Without a heatsink, it hit 75°C and started throttling within ten minutes of a large file copy. After installing a simple heatsink, the temperature never went above 60°C, and the drive maintained its full speed throughout the entire process.

Scenarios Where You Might Not Need an SSD Heatsink
While a heatsink is critical for performance users, it's not a mandatory component for everyone. A balanced perspective is key to determining if an SSD heatsink is worth it for you. There are plenty of situations where you can safely go without one and save a little money.
- General Everyday Use: If your computer usage consists mainly of web browsing, sending emails, writing documents, and watching videos, your SSD will rarely be under enough load to overheat.
- SATA SSDs: The older 2.5-inch SATA SSDs and even M.2 SATA drives run much cooler than their NVMe counterparts. They do not generate enough heat to require a dedicated heatsink.
- Motherboards with Included Heatsinks: Many modern motherboards come with built-in M.2 heatsinks or "shields." These are often more than adequate for most NVMe drives, so check your motherboard's features before buying a separate one.
- PCs with Excellent Airflow: If you have a large case with multiple fans creating strong, positive airflow, the moving air might be enough to keep your NVMe SSD cool under light to moderate workloads.
For the average user, the performance benefits of a heatsink will likely go unnoticed. The drive simply won't get hot enough for thermal throttling to become an issue. In these cases, the money might be better spent elsewhere in your build.

How to Install an SSD Heatsink
Installing an SSD heatsink is a straightforward process that usually takes less than five minutes. It’s a great, simple upgrade that can have a noticeable impact. Here is a quick guide to get you started.
- Prepare Your Workspace: Make sure your PC is turned off, unplugged, and you've grounded yourself to prevent static discharge.
- Unpack the Heatsink: Your heatsink will typically come with a top plate, a bottom plate (if applicable), thermal pads, and screws.
- Apply the Thermal Pad: Peel the protective film from one side of the thermal pad and carefully place it onto your SSD, covering the controller and NAND flash chips. Then, peel the film from the other side.
- Assemble the Heatsink: Place the SSD with the thermal pad onto the bottom plate of the heatsink (if it has one). Then, place the top part of the heatsink over it, ensuring it makes good contact.
- Secure the Heatsink: Use the provided screws to clamp the heatsink pieces together, sandwiching the SSD firmly but gently. Do not overtighten the screws.
- Install in Your PC: Install the assembled SSD with its new heatsink into the M.2 slot on your motherboard and secure it with the motherboard's M.2 screw.
That’s it! Your SSD is now better equipped to handle heat, ensuring it runs at its best when you need it most. This simple installation further proves why an SSD heatsink is worth it for those seeking maximum performance.

Frequently Asked Questions
Does an SSD heatsink improve lifespan?
Yes, it can. Consistently running electronics at lower temperatures can help reduce wear on the components over the very long term, potentially extending the lifespan of your drive.
Can a heatsink make my SSD slower?
No, quite the opposite. A heatsink does not slow down an SSD; it prevents the drive from slowing itself down due to thermal throttling, thereby helping it maintain its maximum speed.
Do all motherboards support SSD heatsinks?
Most modern motherboards with M.2 slots have enough physical clearance to support an SSD heatsink. However, it's always wise to check for obstructions near the M.2 slot, like a large graphics card.
Is the heatsink that comes with my motherboard good enough?
For most users and most drives, yes. The integrated heatsinks provided with motherboards are generally sufficient for preventing thermal throttling during typical use and even heavy gaming.
Can I use an NVMe SSD without a heatsink?
You absolutely can. For light to moderate use, an NVMe SSD will function perfectly fine without a heatsink. It is only under sustained, heavy workloads that thermal throttling becomes a concern.
Conclusion
So, is an SSD heatsink worth it? For power users, gamers, and content creators pushing their systems to the limit, the answer is a resounding yes. It’s a small, affordable investment that acts as insurance for your SSD's performance, ensuring you get the speeds you paid for when it matters most. For the casual user, it's more of an optional upgrade that provides peace of mind but may not deliver a noticeable difference in day-to-day use.
Before you make a purchase, take a moment to evaluate your own needs. Consider your workload, your PC's internal airflow, and whether your motherboard already includes a solution. By making an informed choice, you can ensure your system is perfectly balanced for performance and reliability.
Have you noticed a difference with an SSD heatsink in your own build? Share your experience in the comments below