If your team is spread across different locations, keeping your company’s data safe and accessible is crucial. You need a cloud database that not only protects your information but also supports the way your remote workforce operates.
Imagine a system that scales effortlessly as your business grows, keeps your data secure from threats, and lets your team collaborate without a hitch. This is exactly what secure cloud databases offer to distributed remote companies like yours. You’ll discover how choosing the right cloud database can transform your operations, boost productivity, and give you peace of mind knowing your data is always protected and within reach.
Keep reading to find out which solutions fit your needs best and how to make security a top priority for your distributed team.

Credit: cyberpress.org
Distributed Cloud Databases
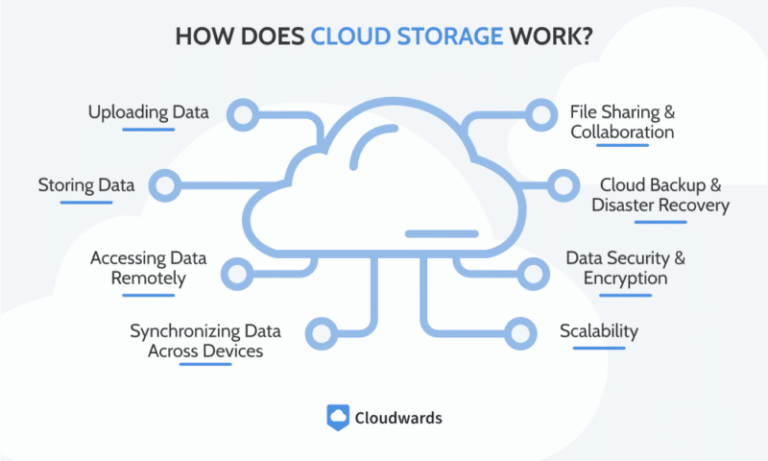
Distributed cloud databases store data across multiple servers worldwide. This setup supports remote teams by keeping data close to users. It improves speed and reliability while ensuring data safety. These databases handle large volumes of data and traffic from different locations. They also allow companies to scale their operations smoothly. Security features protect sensitive information in distributed environments.
Nosql Examples
NoSQL databases suit flexible and unstructured data needs. Examples include MongoDB, Cassandra, and DynamoDB. These databases handle large data sets and high traffic well. They store data in formats like documents, key-value pairs, or graphs. NoSQL databases are good for fast development and scaling. Many cloud providers offer managed NoSQL services for ease.
Distributed Sql Databases
Distributed SQL databases combine traditional SQL with cloud scaling. They offer strong consistency and support complex queries. Examples include Google Cloud Spanner and YugabyteDB. These systems spread data across locations but act as one database. They fit applications needing both scalability and transactional accuracy. Distributed SQL helps maintain data integrity worldwide.
Transactional Workloads
Transactional workloads require databases to process many operations reliably. Distributed cloud databases handle these with ACID compliance. This means transactions are atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable. It prevents data errors and ensures accurate business processes. Banks, e-commerce, and remote teams benefit from this reliability. Cloud databases support high transaction rates and quick recovery.

Credit: en.softonic.com
Choosing The Right Cloud Database
Choosing the right cloud database is crucial for distributed remote companies. It affects data security, access speed, and overall efficiency. The choice depends on various factors like data type, management style, and the existing cloud ecosystem. Understanding these elements helps select a database that meets business needs and supports growth.
Relational Vs Nosql
Relational databases organize data into tables with fixed schemas. They ensure data accuracy using ACID properties. This makes them ideal for structured data and complex queries. Examples include Amazon Aurora and Google Cloud SQL.
NoSQL databases handle flexible, unstructured data. They support various data models like documents, key-value, and graphs. NoSQL excels in scalability and speed for big data or real-time apps. MongoDB Atlas is a popular NoSQL option.
Managed Vs Self-managed
Managed databases are cloud services that handle maintenance, backups, and updates. They reduce the operational burden and let teams focus on development. Examples include Amazon RDS and Azure SQL Database.
Self-managed databases require in-house teams to manage setup, scaling, and security. This option offers more control but needs technical expertise. It suits companies with specific customization needs.
Scalability And Performance
Scalability ensures the database handles growth in users and data smoothly. Performance depends on fast data retrieval and processing. Distributed SQL databases like Google Cloud Spanner provide strong scalability with consistent performance.
Serverless options automatically adjust resources based on demand. Amazon Aurora offers high performance with options for automatic scaling, supporting fluctuating workloads efficiently.
Cloud Ecosystem Integration
Integrating the database with the existing cloud ecosystem improves efficiency. It allows smooth data flow between services like storage, analytics, and security tools. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer databases optimized for their platforms.
Choosing a database aligned with the cloud provider simplifies management. It also leverages built-in features such as monitoring and identity management. This improves security and reduces setup time.
Top Cloud Database Providers
Choosing the right cloud database provider is vital for distributed remote companies. Reliable and secure cloud databases ensure smooth data access across multiple locations. Top providers offer strong security, easy management, and global scalability. These features support remote teams and protect sensitive information.
Below are some leading cloud database providers that cater to diverse business needs. Each provider brings unique strengths in security, performance, and flexibility.
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a wide range of cloud databases. Amazon Aurora is a popular choice for relational databases. It delivers high performance and automatic scaling. AWS also provides DynamoDB for NoSQL needs. This service is fully managed and supports fast, flexible data access. AWS databases include built-in security features to protect data.
Google Cloud
Google Cloud offers Cloud SQL for managed relational databases. It supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. Cloud Spanner provides a distributed SQL database with global scalability. Google Cloud ensures data encryption and strong access controls. Their cloud database services integrate well with other Google tools and services.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure provides Azure SQL Database as a fully managed relational service. It offers high availability and automatic backups. Cosmos DB supports multiple data models, including document and key-value stores. Azure’s security measures include threat detection and data encryption. Azure databases integrate easily with Microsoft products.
Mongodb Atlas
MongoDB Atlas is a leading NoSQL cloud database service. It handles flexible document data structures efficiently. Atlas offers global distribution and automated scaling. Security features include encryption at rest and in transit. This service suits companies needing fast, schema-free data storage.
Security Measures
Security measures are crucial for cloud databases used by distributed remote companies. These measures protect sensitive data and ensure smooth business operations. Strong security helps prevent data breaches and unauthorized access. It builds trust among remote teams and customers. Understanding key security features is essential for any organization using cloud databases.
Data Encryption
Data encryption scrambles information so only authorized users can read it. Cloud databases use encryption both during data transfer and storage. This protects data from hackers or accidental leaks. Encryption keys are managed securely to avoid misuse. Strong encryption standards keep data safe across all locations.
Access Controls
Access controls limit who can view or change data in the cloud database. Role-based access assigns permissions based on job needs. Multi-factor authentication adds a second layer of security. These controls reduce the risk of insider threats and external attacks. Regular audits ensure access rules stay up to date.
Compliance Standards
Compliance standards ensure cloud databases follow legal and industry rules. Examples include GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. Meeting these standards protects user privacy and financial data. Cloud providers often offer tools to help companies maintain compliance. Adhering to standards reduces risks and builds customer confidence.
Threat Detection
Threat detection systems monitor cloud databases for unusual activity. They identify potential cyberattacks or data leaks early. Alerts allow teams to respond quickly and limit damage. Automated tools use machine learning to improve detection accuracy. Continuous monitoring keeps the database environment secure.
Optimizing Performance For Remote Teams
Optimizing performance in secure cloud databases is crucial for remote teams. Distributed remote companies depend on fast, reliable access to data. Efficient database management supports smooth collaboration across locations. Low latency, balanced workloads, and strong backup plans all contribute to this goal.
Latency Reduction
Latency affects how quickly remote teams access data. Cloud databases store data in multiple locations near users. This reduces the time it takes to fetch information. Techniques like data caching and edge computing help lower delays. Faster response times improve productivity and user experience.
Load Balancing
Load balancing spreads database traffic evenly across servers. It prevents any single server from becoming overloaded. This ensures stable performance during peak usage times. Remote teams experience fewer slowdowns or interruptions. Load balancing also enhances system reliability and uptime.
Backup And Recovery
Regular backups protect data from loss or corruption. Cloud databases automate backup processes for remote teams. Quick recovery options restore data with minimal downtime. This safeguards business continuity and trust. Reliable backup systems are vital for secure cloud environments.
Cost Management Strategies
Managing costs is vital for distributed remote companies using secure cloud databases. Efficient cost strategies help avoid overspending and improve resource use. This section covers key methods to control expenses while keeping performance strong.
Resource Allocation
Assign only the necessary resources to your cloud databases. Avoid over-provisioning by analyzing actual usage patterns. Choose the right database size and storage based on workload demands. Proper resource allocation reduces waste and lowers monthly bills. Review and adjust allocations regularly to match changing needs.
Scaling Options
Use scalable cloud database services that grow with your company. Opt for automatic scaling to handle traffic spikes without manual intervention. Scale down during low usage times to save money. Consider serverless database options that charge based on actual usage. Flexible scaling ensures cost efficiency and consistent performance.
Monitoring And Alerts
Set up monitoring tools to track database performance and costs in real time. Use alerts to notify your team about unusual usage or rising expenses. Early detection of issues helps prevent unexpected bills. Regular monitoring allows proactive cost management and keeps your budget under control.
Future Trends In Cloud Databases
The future of cloud databases holds exciting changes for distributed remote companies. These trends focus on improving security, scalability, and ease of management. Cloud databases will become smarter and more flexible to meet growing business needs. Companies can expect better ways to handle data across multiple clouds and use automation to reduce manual work.
Multi-cloud Strategies
Using multiple cloud providers helps companies avoid dependency on one platform. Multi-cloud strategies improve availability and reduce risks of downtime. Data can move smoothly between clouds, enhancing disaster recovery plans. This approach also helps companies choose the best services from each provider. Security remains a priority, with encryption and access controls managed across clouds.
Serverless Databases
Serverless databases remove the need to manage servers or infrastructure. They automatically scale based on demand, saving costs during low usage. Developers focus on building applications, not maintaining databases. These databases offer fast deployment and easy integration with cloud services. Security features are built-in, ensuring data stays protected without extra effort.
Ai And Automation Integration
Artificial intelligence helps optimize database performance and security. Automation handles tasks like backups, updates, and threat detection. AI tools analyze data patterns to improve query speed and reduce errors. Automated alerts notify teams of any unusual activity instantly. This integration reduces human errors and frees up time for strategic work.

Credit: cyberfortress.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Example Of A Distributed Cloud Database?
An example of a distributed cloud database is Google Cloud Spanner. It offers global scalability and strong consistency for transactional workloads. Other popular examples include Amazon Aurora, MongoDB Atlas, Cassandra, and Azure Cosmos DB. These databases support distributed data storage and seamless cloud integration.
What’s The Best Cloud Database For Tech Companies?
The best cloud database for tech companies depends on needs. Amazon Aurora suits scalable relational data. MongoDB Atlas offers flexible NoSQL. Google Cloud SQL and Azure SQL Database provide fully managed services with seamless cloud integration.
Is A Cloud Database Secure?
Cloud databases use encryption, access controls, and regular audits to protect data. They offer robust security but require proper configuration.
Does Google Have A Relational Database?
Google offers relational databases like Cloud SQL and Cloud Spanner. Cloud SQL supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. Cloud Spanner provides a scalable, distributed SQL database with strong consistency. Both services serve different relational database needs on Google Cloud Platform.
Conclusion
Securing cloud databases is vital for remote, distributed teams. Choose databases that fit your company’s needs and scale easily. Prioritize security features to protect sensitive data from threats. Managed cloud databases reduce your workload and increase reliability. Using the right tools helps your team work smoothly from anywhere.
Stay updated on best practices to keep data safe and accessible. Secure cloud databases support growth and remote collaboration effectively.